CSIR-NEERI OxiMax Electrolytic Defluoridation (EDF) System
It is estimated that in India, 62 million people including 6 million children suffer from Fluorosis, which is caused due to the consumption of water that is contaminated with excessive fluoride.
To curb this increasing menace of fluoride in the country’s groundwater, CSIR-NEERI (National Environmental Engineering Research Institute) and HES Water Engineers India Pvt. Ltd. has joined hands to treat potable water through effective, sustainable, and economical technologies.
To make clean and pure drinking water available to the people of India, CSIR-NEERI has transferred its technology for Electrolytic Defluoridation to HES Water Engineers for commercial manufacturing and installation of these units in areas that have a high fluoride content in water.
CSIR-NEERI Electrolytic Defluoridation (EDF) System
What is Electrolytic Defluoridation (EDF)?
As a water purification system, the Electrolytic defluoridation process is based on the principle of electrolysis, wherein aluminium plate electrodes are placed in the raw water containing excessive fluoride. During this process, the electrodes produce Aluminium Hydroxide, which helps coagulate impurities and fluorides together, forming flocs. This floc gets settled in the water tank, which is then filtered out using a multigrade sand filter.
The Electrolytic Defluoridation (EDF) System is suitable for areas where water is excessively contaminated by fluoride. Being an advanced technology, this system works on both electricity and solar photovoltaic systems. Thus, making it a great choice for even those areas that have power supply issues.
How Does Electrolytic Defluoridation Work?
The Electrolytic Defluoridation process not only removes excess fluoride but also helps bring down the bacterial load of raw water. As seen above, during the process of electrolysis, the anode gets ionized and fluoride is removed by complex formation, adsorption, precipitation, coagulation, and settling.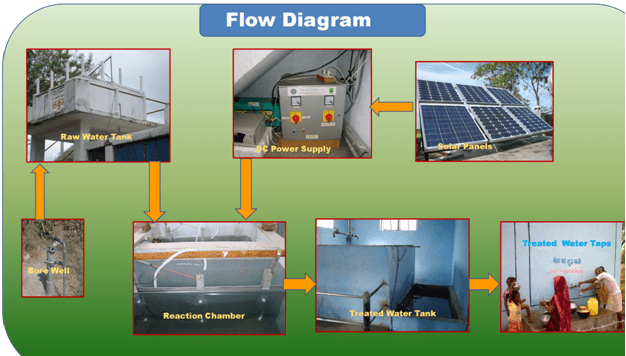 The chemical reaction taking place during electrolytic defluoridation is as following:
The chemical reaction taking place during electrolytic defluoridation is as following:
Anode: AI(s) Al 3 + + 3e-
Cathod: 2H2O +2e- H2+2OH-
The Al3+ ions further react to form AI (OH)3 floes, which adsorb the fluoride ions present in the water resulting in the formation of sludge.
Al3 + + 3H20(S)AI(OH)3(S) + 3H+
AI(OH) 3 + xF-AI(OH)3-xFx +OH-
Direct Current (20-30 amp) required for the electrolytic process is generated either by conversion of AC electric supply or by DC conversion unit of required capacity or by a solar photovoltaic system consisting of solar panel, charge controller and battery.
Sludge Disposal
Studies conducted on the process of Electrolytic defluoridation has found that post sludge generation, the fluoride doesn’t leach back into the water. Along with installing the EDF system, a small sand sludge drying bed can also be constructed outside the plant, wherein the sludge slurry can be put to drain, thereby allowing the sludge to dry. The dry sludge can then be used for brick making or can be safely disposed of in landfills.
Advantages of Electrolytic Defluoridation (EDF) System
- The technology is developed by CSIR-NEERI – India’s premier research institute.
- It is ideal for treating raw water with fluoride concentration up to 10mg/lit.
- It is easy to operate, even by an unskilled person and requires minimum maintenance.
- It produces portable water with a palatable taste.
- Compared to conventional methods, the sludge regenerated is 60-70% less.
- It can reduce fluoride to as low as 0.25 mg/l while also lowering the bacterial count (total coliform and E-Coli).


